As lovers of great design, Optima’s appreciation for both architecture and art itself runs deep, and there’s no better place to indulge this passion than at a modern museum of art. And with modern art and Modernist architecture sharing so much in common, it’s no wonder that many of these institutions are often housed in innovative and captivating buildings. Today, we’re taking a look at some of the best modern museums around the world — from the collections they contain to the structures that define them.
Guggenheim Museum Bilbao – Bilbao, Spain
The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao is a museum of modern and contemporary art designed by Canadian-American architect Frank Gehry, located in Bilbao, Spain. You’ll recall from our Subsects of Modernist Architecture Series that Gehry was part of the Deconstructivism movement on Modernism in the 1980s. This museum, established in 1997, boasts an impressive collection of modern art, as well as site-specific installations from artists such as Jeff Koons. The building itself has been described as “the greatest building of our time” by architect Philip Johnson, and “a fantastic dream ship of undulating form in a cloak of titanium,” by critic Calvin Tomkins in The New Yorker.
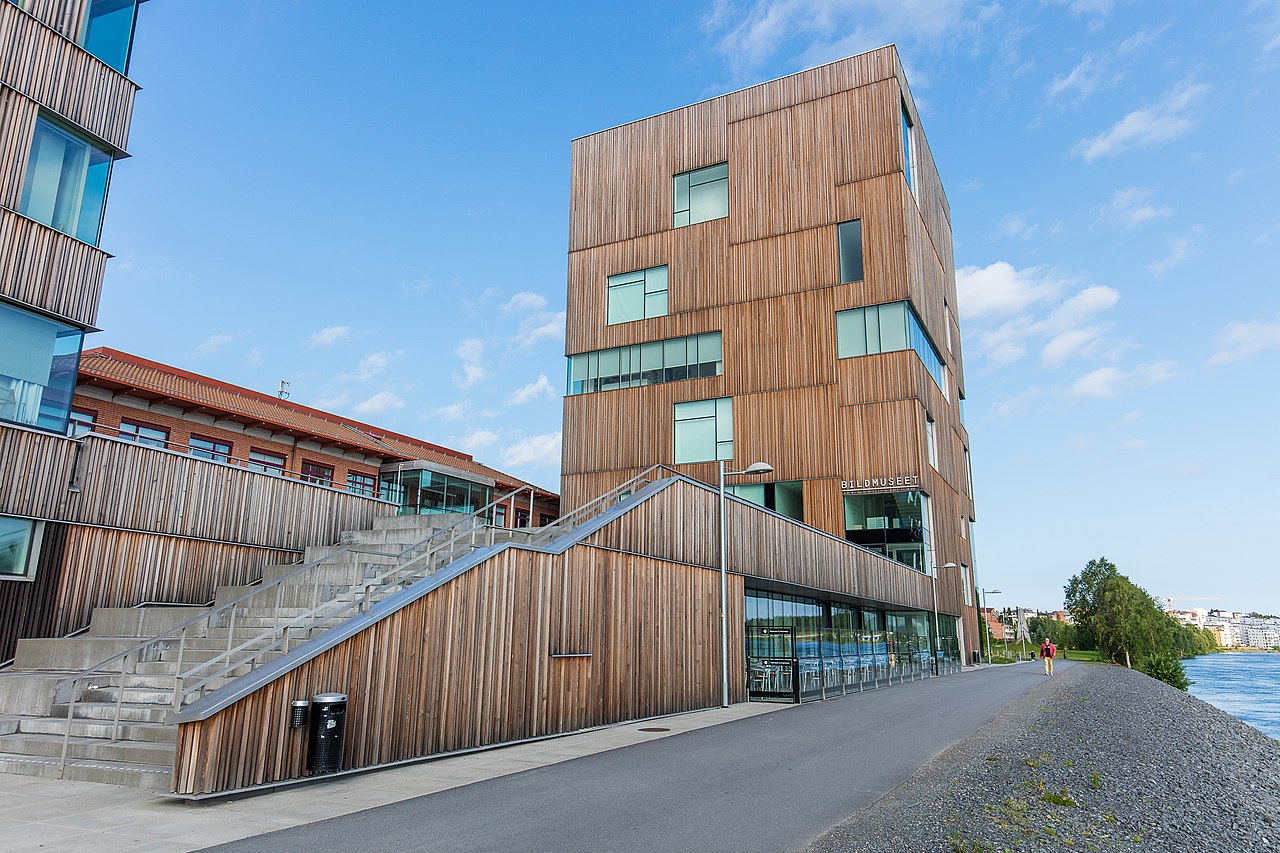
Bildmuseet – Umeå, Sweden
Bildmuseet is one of Sweden’s foremost venues for international contemporary art, a part of Umeå University and the public heart of its arts campus. The strikingly Modern building was designed by Henning Larsen Architects in collaboration with White. A living and breathing work of art itself, the building’s facade is made of Siberian larch wood that fades to a silver-grey color over time. In its lifetime, Bildmuseet was nominated in 2013 for the Swedish Kasper Salin Prize and the European Mies van der Rohe Prize and has been described as one of the world’s most beautiful university museums.

Zeitz Museum of Contemporary Art Africa – Cape Town, South Africa
Zeitz Museum of Contemporary Art Africa (or Zeitz MOCCA, for short) is a contemporary art museum in Cape Town, South Africa, and boasts the title of being the largest museum of contemporary African art in the world. The building, which was commissioned through a public/private partnership between the V&A Waterfront and German businessman, Jochen Zeitz, is actually made from a converted historic 1921 grain silo. According to Zeitz MOCAA records, “The architects, Heatherwick Studio, aimed to conserve and celebrate the original structure’s industrial heritage, while simultaneously excavating large open spaces from the 42 densely-packed concrete cylinders from which it was comprised.”
Niteroi Contemporary Art Museum — Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
It’s no surprise that the Niteroi Contemporary Art Museum, located in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, is one of the city’s main landmarks. The futuristic building was designed by Oscar Niemeyer with the assistance of structural engineer Bruno Contarini. Thanks to its strategic design, this museum offers more than just art to admire — the tall, angled windows offer sweeping views of Guanabara Bay and Sugarloaf Mountain. Beneath the structure, architect Niemeyer also designed a reflecting pool that surrounds the cylindrical base “like a flower.”
As an artform all on its own, the architecture of these museums stands strong alongside their impressive modern art collections.