Our “Subsects of Modernist Architecture” series explores the many trickle-down pockets of Modernist design throughout the years. In this last installment of the series, we’re taking a look at the late-century styles that have continued to carry on the legacy of Modernist design — and that will continue to influence and inspire many generations and future subsects to come.
Postmodernism
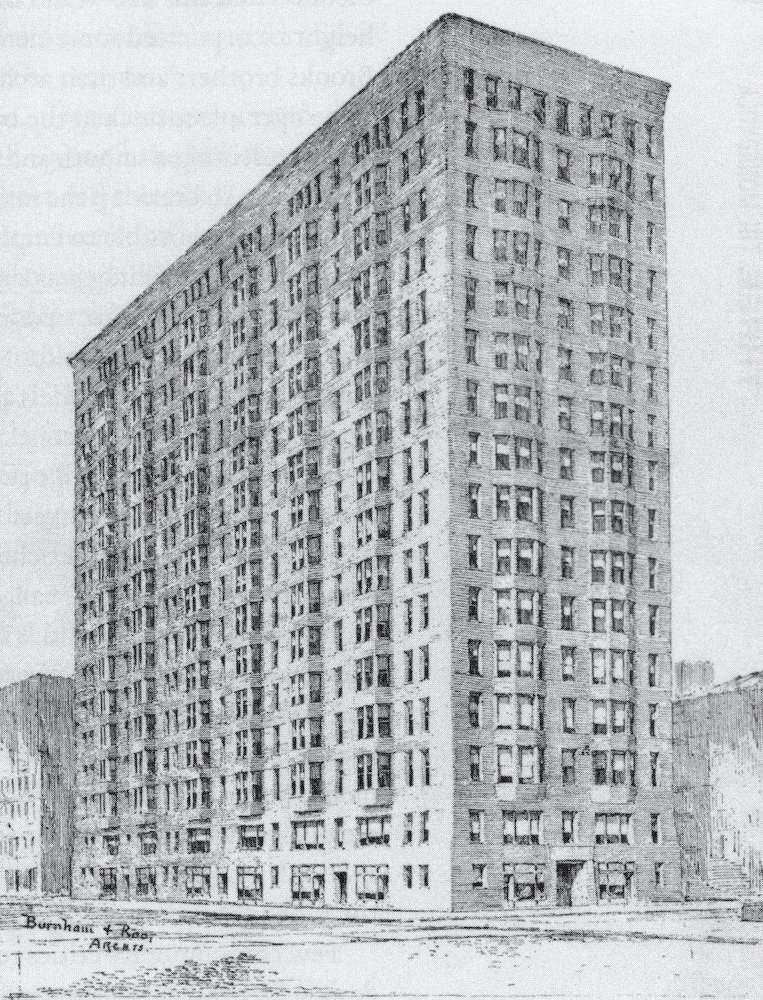
Postmodernist architecture emerged in the 1960s as a reaction to the severe and repetitive nature of Modernist architecture, particularly the International Style. While Modernist had previously been celebrated for its lack of ornamentation and rigid uniformity, architects in the camp of Postmodernism were ready for a boisterous change.
The movement was first introduced by architect and urban planner Denise Scott Brown and architectural theorist Robert Venturi in their seminal work, Learning from Las Vegas. In this timeless book, Brown and Venturi doubled down on their ideas about postmodernist design, which Venturi formalized in his later book, Complexity and Contradiction in Architecture. He wrote:
“I am for messy vitality over obvious unity… I prefer ‘both-and’ to ‘either-or’, black and white, and sometimes gray, to black or white… An architecture of complexity and contradiction must embody the difficult unity of inclusion rather than the easy unity of exclusion.”
While Mies van der Rohe’s famous adage was “less is more”, Venturi’s pushback saying became “less is a bore.” As Postmodernism flourished in the 1980s and 1990s, Brown & Venturi led the charge alongside other architects such as Michael Graves, Philip Johnson and Charles Moore.
High-tech
As Postmodernist thinking evolved during the 1970s, High-tech architecture (also known as Structural Expressionism) was born. Just as the name suggests, High-tech began to incorporate the latest technological innovations building materials into its design. Like traditional Modernist architecture, High-tech commonly employed steel, glass and concrete in building exteriors — but to much different effect. Still, the influence of Modernist masters such as Le Corbusier, Walter Gropius and Mies van der Rohe remains evident.
High-tech architecture was heavily influenced by factory aesthetics, incorporating large central spaces, hanging or overhanging floors, and highly-adaptable, reconfigurable spaces as key design elements. The polycentric usage of these central spaces was defined by the term “omniplatz” — referring to the idea that a building shouldn’t have one, defined function, but rather remain able to perform a range of functions. Feelings of openness, transparency and honesty were central to High-tech design, coupled with considerations of adaptability and sustainability. Despite its technological roots, this subsect was indeed modeled on highly human-centric thinking.
Deconstructivism
Deconstructivism appeared on the scene in the 1980s. Inspired by its Postmodernist counterparts, Deconstructivism seeks to imply fragmentation of buildings through an absence of obvious harmony, continuity or symmetry. The result is a feeling of unpredictability and carefully controlled chaos all at once.
The name was earned by the movement’s chief aims to “disassemble” architecture and to break traditional rules and boundaries. The architectural movement also heavily drew inspiration from French philosophy. Key architects who worked in this style include Zaha Hadid, Peter Eisenman, Frank Gehry, Rem Koolhaas, Daniel Libeskind and Bernard Tschumi.
All these styles and more make up the legacy that created Modernist design as we know it today.