Chicago is home to a vast array of architectural diversity, from Modernism to Prairie School and beyond. Although no two city skyscrapers are the same, Marina City is one building that particularly stands out. Built by American architect Bertrand Goldberg, the industrial series of towers represent his unique mark on Chicago architecture. Today, we’re taking a closer look at Goldberg’s life and work.

Early Life and Architectural Beginnings
Born local to Chicago in 1913, Bertrand Goldberg left the US for Germany at the ripe young age of eighteen in 1932. There, he studied at the Bauhaus and worked at the small architectural office of Bauhaus director Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. Like many others studying and working in Germany during that period, Goldberg eventually had to flee the country under mounting political pressure and civil unrest. After a brief stint in Paris, Goldberg returned to his hometown in Chicago to continue his career.
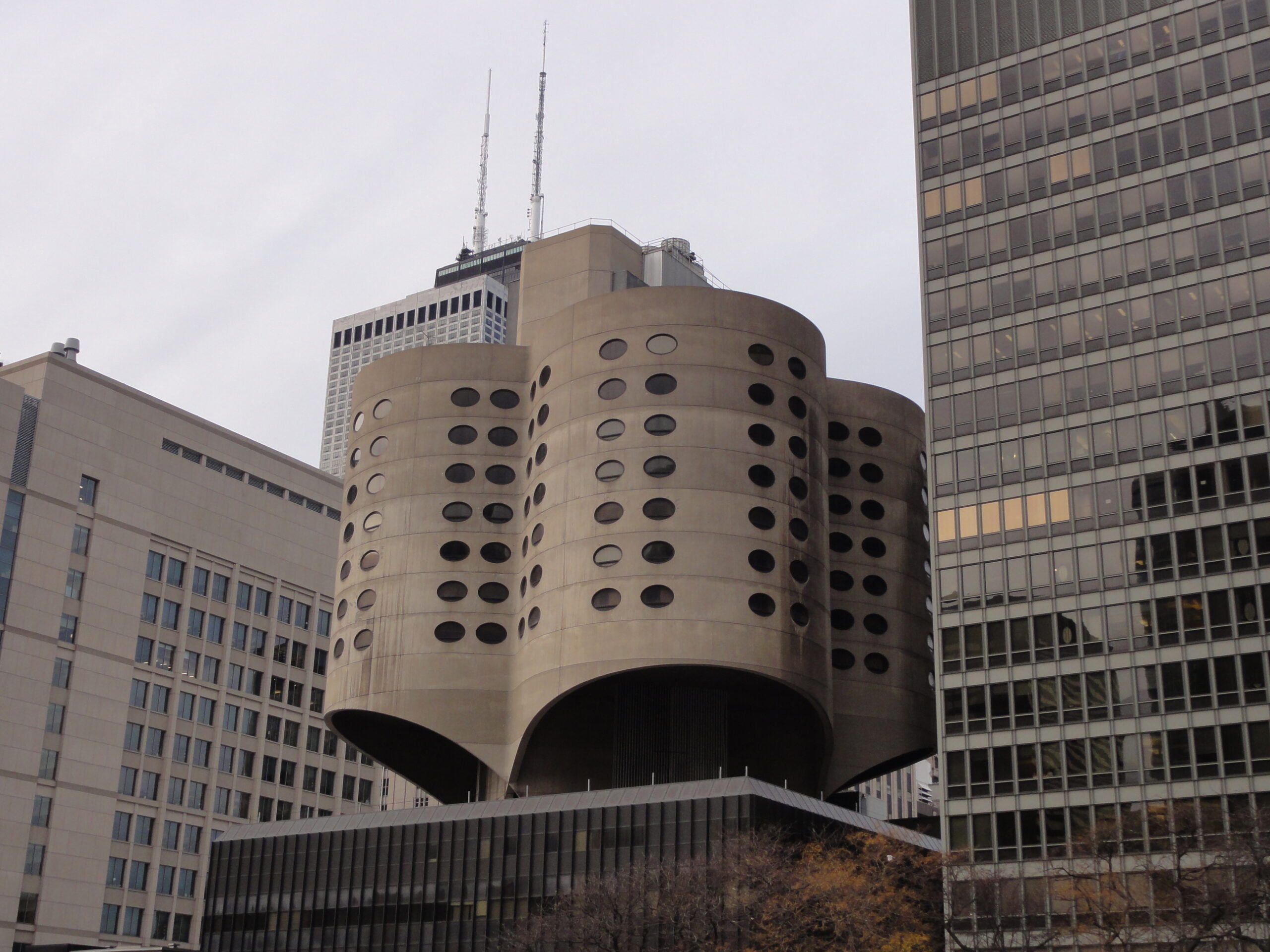

The Work of Bertrand Golberg
At only 23 years old, Goldberg opened his own architectural office in Chicago. He was most known for his innovative structural solutions to complex problems, with commissions that included designing an easily transportable structure for the North Pole chain of ice cream shops as well as many prefabricated projects and mobile vaccine laboratories for the US government.
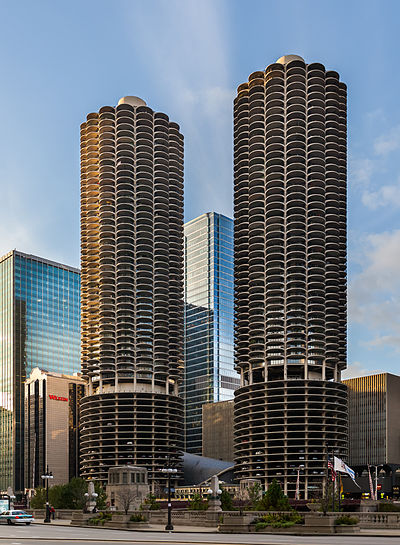
His work was always experimental, testing out ways to create unconventional forms through extremely conventional and mundane materials. His most popular project is Marina City, often referred to as the “corn cobs,” which stand out in sharp relief against the Chicago riverfront.
Marina City is a mixed-use complex of five concrete towers, built in 1961-1964, that has continued to change and evolve over time. Goldberg’s original plan was complete with an office building, theater, public pedestrian plaza, an active rail line, a marina, an ice skating rink and a bowling alley. Though the rail line and skating rink are no longer standing, the theater remains, converted in the Chicago House of Blues venue.
The success and critical acclaim of Marina City inspired many of Golberg’s later structures, including River City in Chicago and several hospital structures across the country. Though Goldberg died in Chicago in 1977, he has built a lasting legacy and forever left his mark on the Chicago skyline.