At Optima®, we’re always fascinated to spotlight the unique elements of architecture and design that have had a profound impact in history. This time, we’re focusing on the renaissance of a timeless art form that is seamlessly bridging the gap between the traditional and the contemporary — Stained Glass Windows.
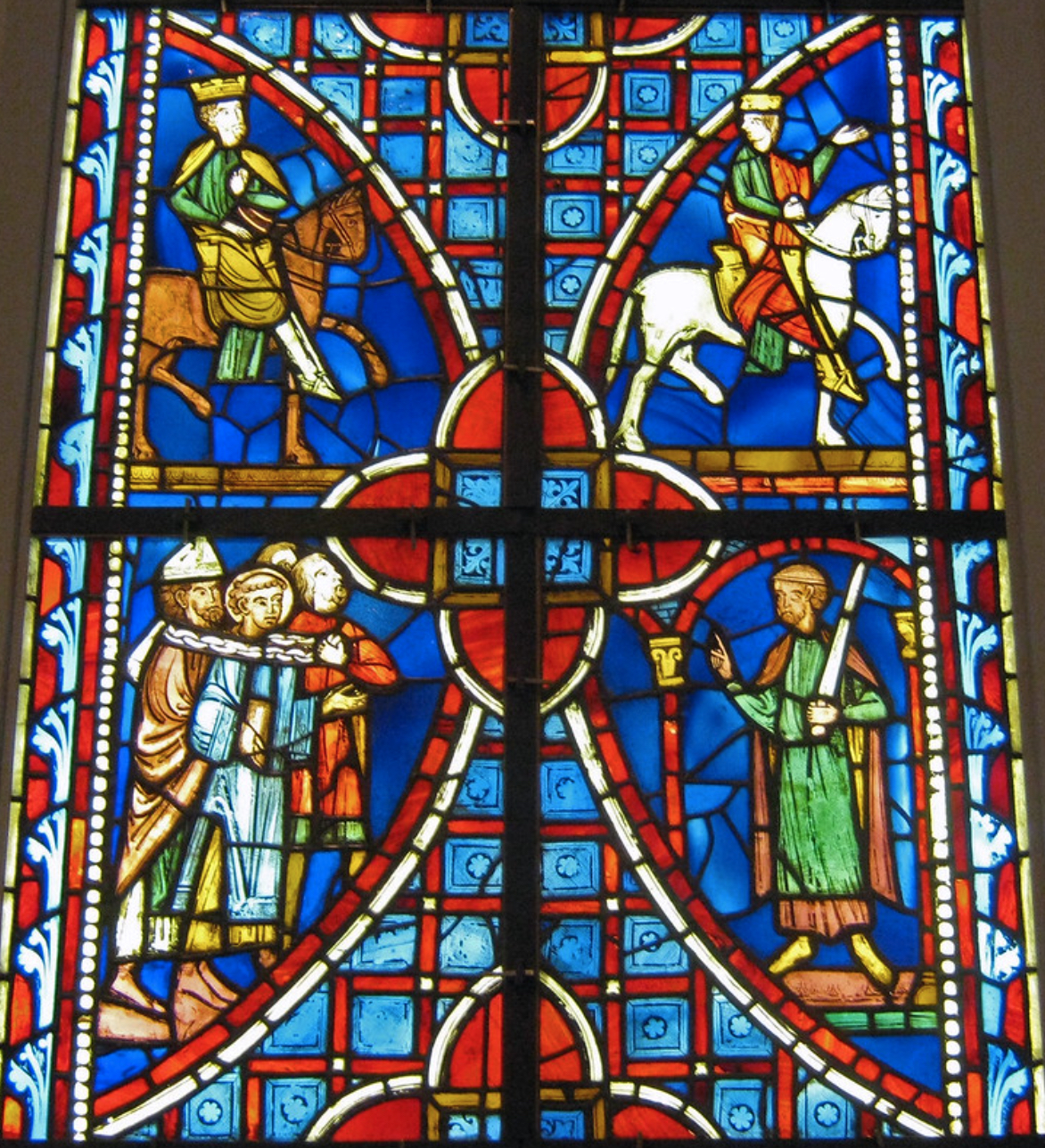
Stained-glass windows, or art glass windows, often appreciated for their utility and beauty, have roots tracing back to ancient Rome. They blossomed into prominence between 1150 and 1500, adorning the cathedrals of Europe with intricate, vibrant patterns. But the modern era is experiencing a resurgence of this art form. Today, stained glass windows aren’t confined to churches or Victorian homes but have made an enchanting comeback in contemporary design.

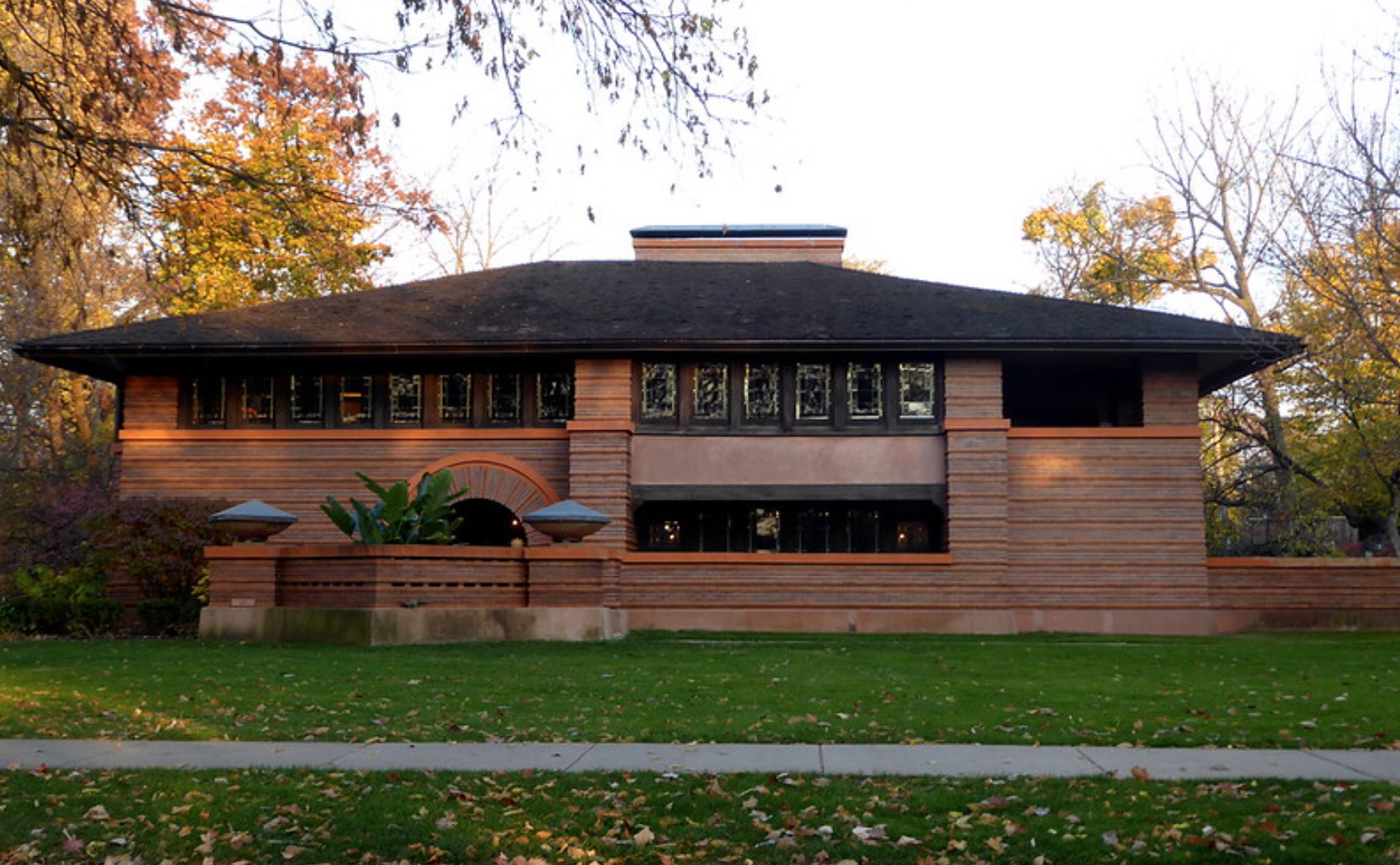
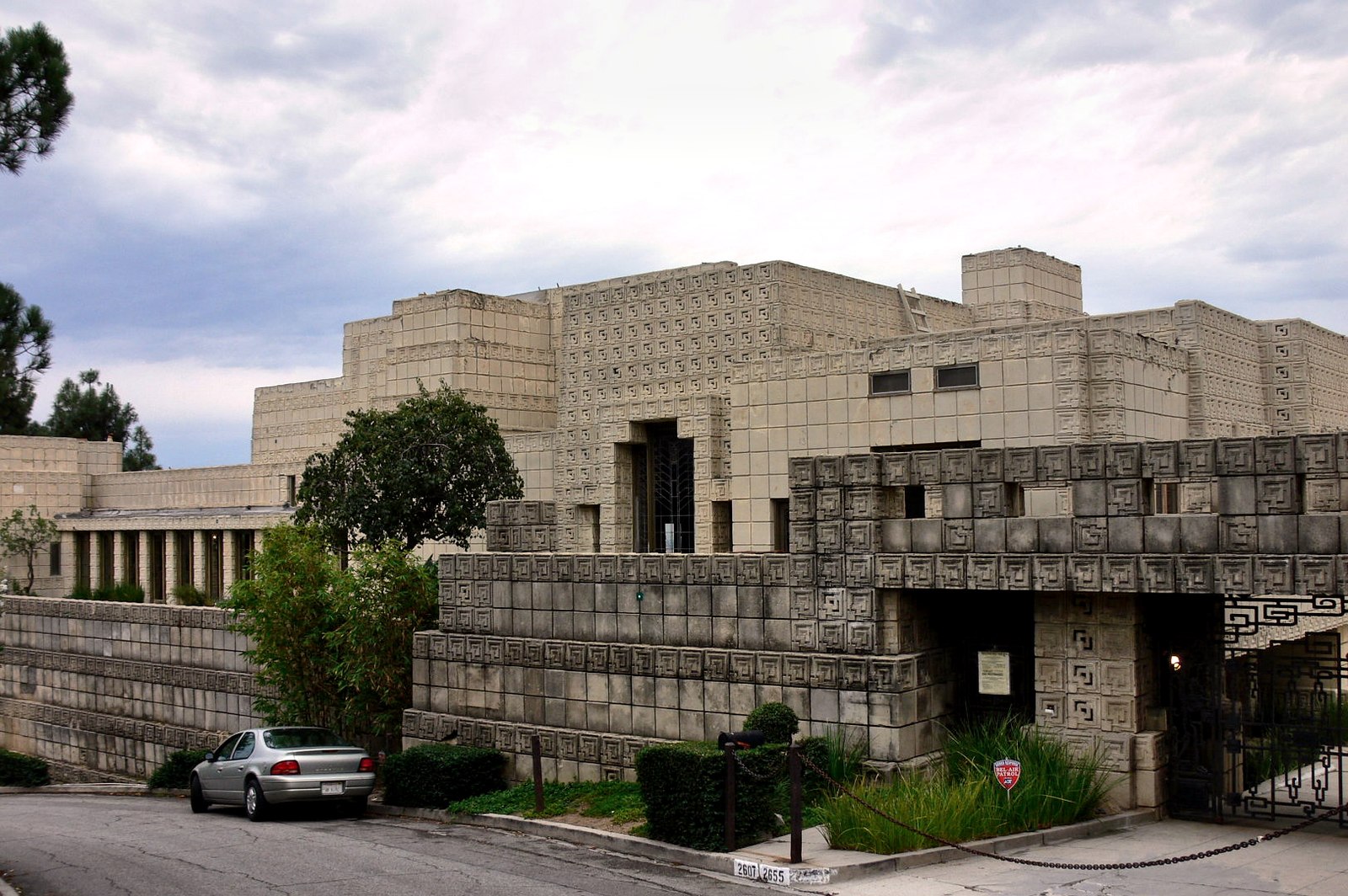
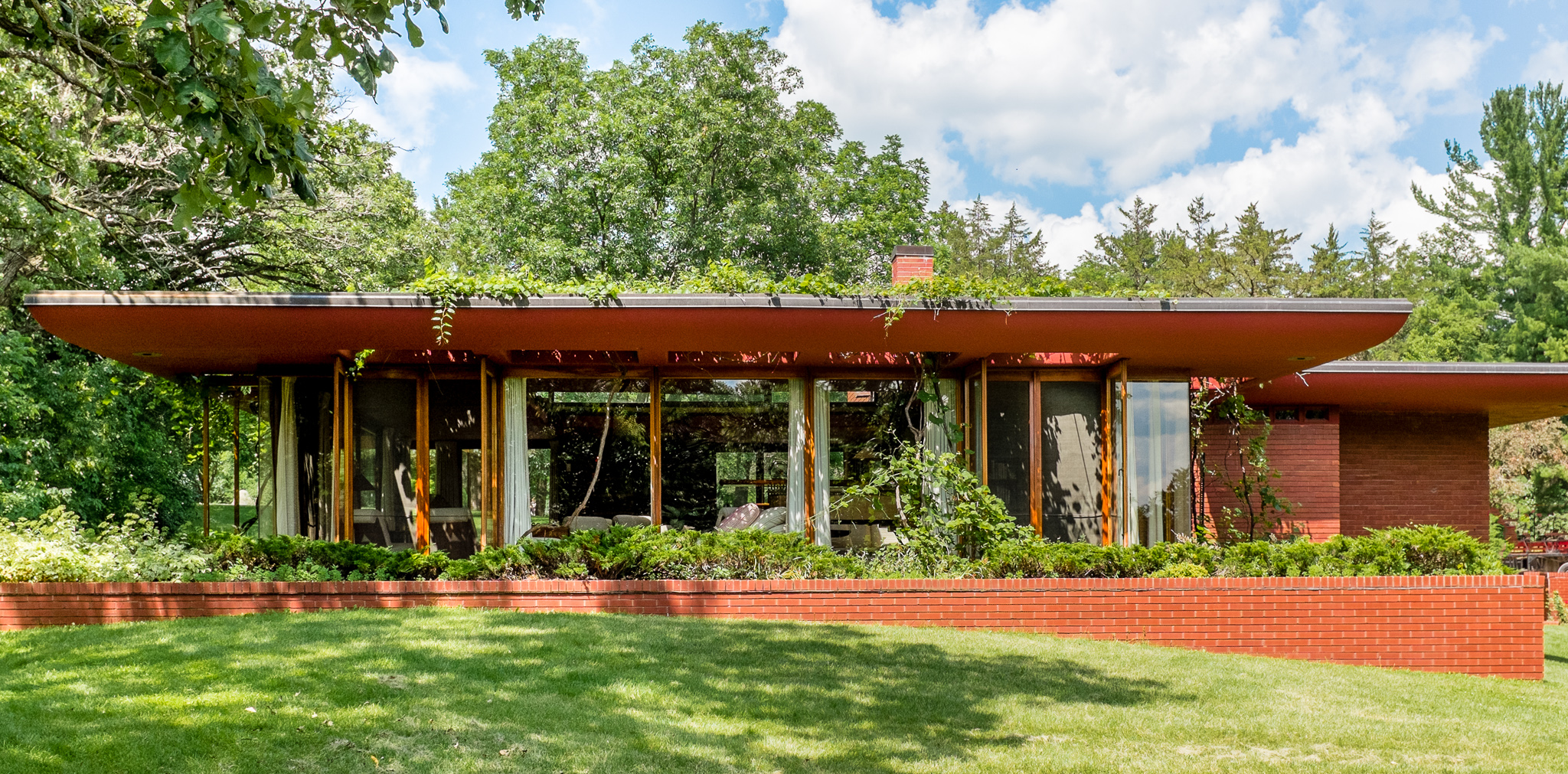
Famed architects have leveraged the beauty of stained glass in their designs. Frank Lloyd Wright, for instance, frequently incorporated art glass into his iconic works, including the remarkable Arthur Heurtley House in Oak Park. Here, he integrated stained glass windows into the home’s design, creating intricate geometric patterns that brought warmth, privacy, and an unparalleled aesthetic charm. The use of art glass also reveals itself in the Oak Circle Historic District, a small grouping of 15 early twentieth-century houses, built primarily in the Craftsmen style with magnificent detailing from the Prairie School of Architecture.

Stained glass windows are more than just pleasing aesthetics. They are crafted with a fascinating process. The basic ingredients for glass, sand, and wood ash are melded into a beautiful symphony of colors with the addition of powdered metals. These pieces of colored glass are assembled into captivating designs that tell stories, highlight themes, or merely add an artist’s touch to any space.
Why are stained glass windows reclaiming their spot in modern design, you ask? Their versatility, for one, is unmatched. Customizable to fit any stylistic preference, they can embody soft, subtle color combinations or bold, elaborate displays. But their versatility extends beyond just aesthetics. Though windows are the most common form, stained glass has been creatively integrated into room dividers, doors, and even fireplace screens.

Photo: Slices of Light, Flickr Creative Commons
Moreover, these artistic installations are a boon to privacy. Stained glass windows can block unattractive views without compromising on natural light. This interplay of privacy and luminosity creates intimate spaces infused with a stunning spectrum of colors.
Stained glass windows also serve as a profitable investment. They’re known to increase the value of your home in more ways than one. From enhancing your home’s curb appeal to augmenting its market and perceived value, stained glass windows serve as an alluring asset.

We’re thrilled to see the innovative ways in which stained glass windows are being used in modern design. Every architectural element tells a story and contributes to the overall narrative of the space. Stained glass windows are a testament to this belief – a beautiful blend of art, history, functionality, and design. In the end, they give us pause, reminding us that while architecture serves as a canvas, it’s our creativity that paints the picture.