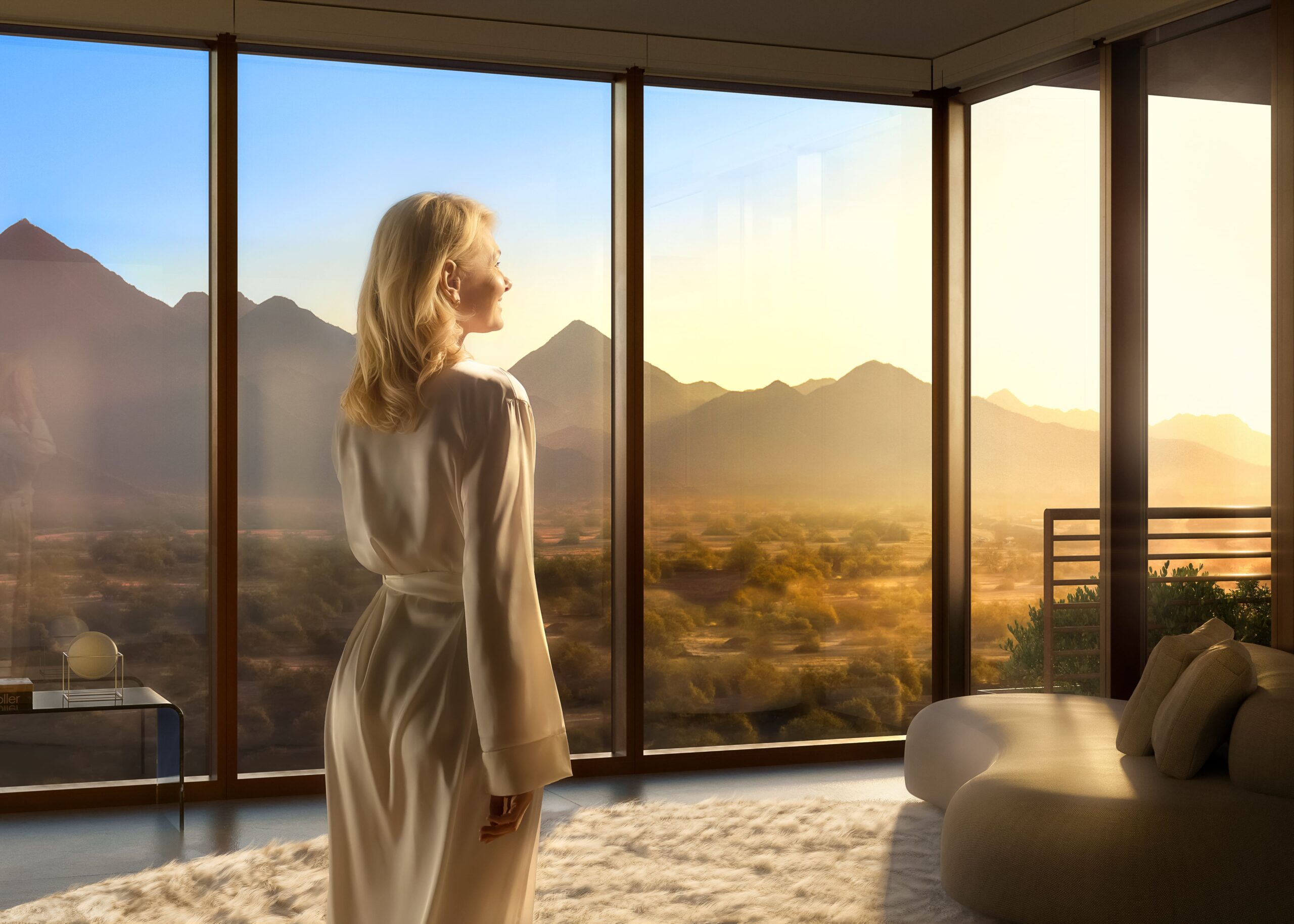
At Optima®, our communities are guided by a deep belief that architecture can nurture, inspire, and elevate the human spirit. This philosophy has long aligned with Modernism’s embrace of light, space, and form. Today, a growing field of study known as neuroarchitecture is helping to explain, through the lens of science, why certain spaces make us feel calm, creative, or connected.
What is Neuroarchitecture?
Neuroarchitecture sits at the intersection of neuroscience, psychology, and architecture. It seeks to understand how the built environment influences brain function and emotional well-being. Using tools like functional MRI scans, eye-tracking studies, and biometric sensors, researchers can observe how different architectural elements—light, ceiling height, materials, spatial flow—affect cognitive performance, stress levels, and even hormone production.
At its core, neuroarchitecture is about recognizing that our brains are not passive observers of space. Instead, they are actively shaped by it. This emerging field offers a scientific foundation for what architects and designers have long intuited: the spaces we inhabit affect how we think, feel, and behave.

The Brain’s Response to Space
Research in neuroarchitecture reveals that certain design features can measurably influence brain activity. For example:
- Natural Light: Exposure to daylight regulates our circadian rhythms, boosts serotonin, and can enhance mood and productivity.
- Ceiling Height: Taller ceilings have been linked to more expansive thinking, while lower ceilings can promote focus and concentration.
- Nature Integration: Biophilic design—bringing natural forms, materials, and greenery into a space—reduces stress and promotes cognitive restoration.
- Spatial Flow: Open, interconnected layouts encourage movement, social interaction, and a sense of freedom.
These findings are helping architects make more informed decisions, creating spaces that are not only beautiful but also neurologically supportive.
A New Lens on Modernist Principles
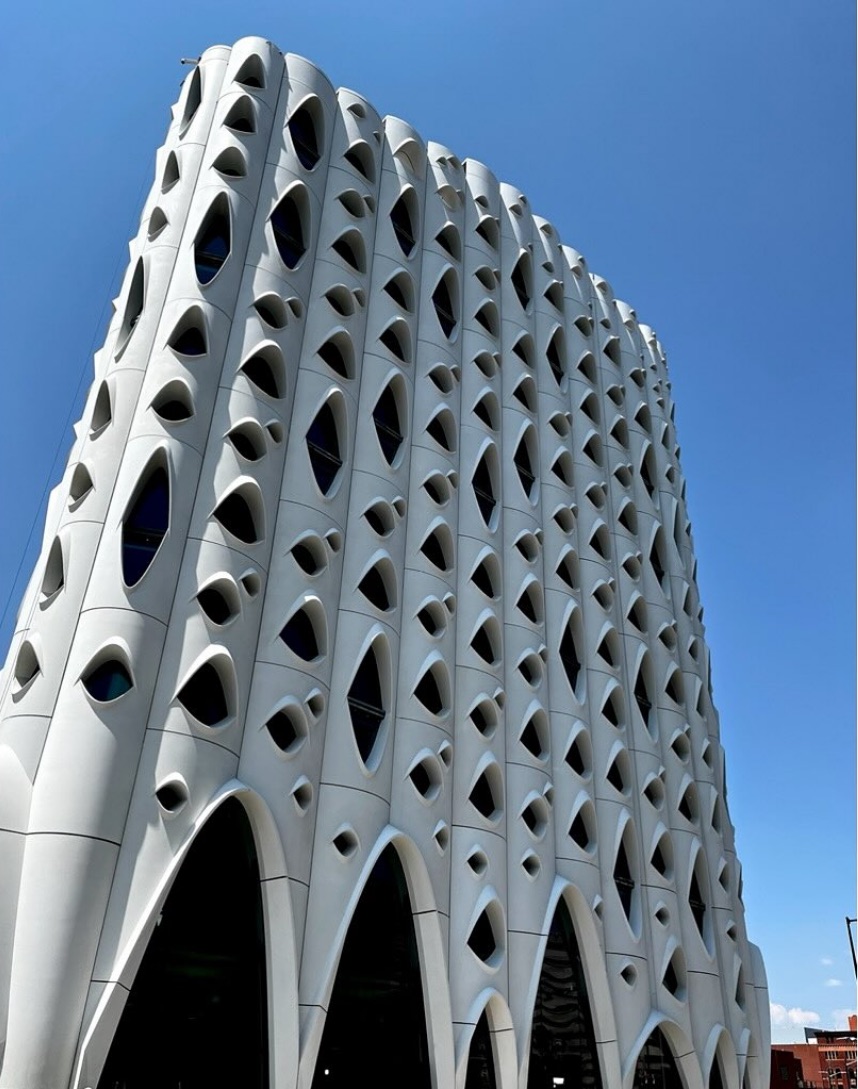
Modernist architecture, with its emphasis on functional beauty, open floor plans, and abundant light, often aligns naturally with neuroarchitectural insights. In Optima® communities, expansive windows flood interiors with daylight, green courtyards and gardens bring nature to residents’ doorsteps, and thoughtful spatial layouts encourage both solitude and connection.
For example, the lush vertical landscaping at Optima Sonoran Village® is not only visually striking—it offers residents a daily, tangible connection to the calming effects of nature. At Optima Verdana®, the indoor–outdoor flow of common spaces provides social engagement opportunities while supporting mental ease and relaxation.
Applications Beyond Residential Design
Neuroarchitecture’s potential extends far beyond homes. In schools, its principles can help create environments that improve focus and learning outcomes. In healthcare, design elements informed by neuroscience can reduce patient anxiety and promote faster recovery. Even in workplaces, carefully tuned lighting, acoustics, and layouts can enhance creativity, collaboration, and employee well-being.
The Future of Building for the Brain
As technology enables us to measure and analyze human responses to space with increasing precision, neuroarchitecture is likely to become an essential part of the design process. Architects and developers will have more data-driven insights to tailor environments to specific human needs—whether that’s reducing stress, encouraging collaboration, or sparking innovation.
For Optima®, this convergence of science and design reinforces a long-held commitment: that great architecture is not just about form, but about the lives lived within it. Neuroarchitecture offers a language and framework for understanding the deep connection between space and self—a connection we have been honoring through Modernist design for decades.
In the end, neuroarchitecture doesn’t replace the artistry of building; it enriches it. By aligning the principles of design with the biology of the brain, we can create spaces that are not only aesthetically compelling, but also profoundly supportive of human well-being—places where people don’t just live, but truly thrive.